Understanding CT Scans for Lung Cancer

Lung cancer remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths globally. Early detection is crucial for increasing survival rates. One of the most significant advancements in modern medicine is the advent of the CT scan for lung cancer, a powerful diagnostic tool that can provide invaluable insights into lung health.
What is a CT Scan?
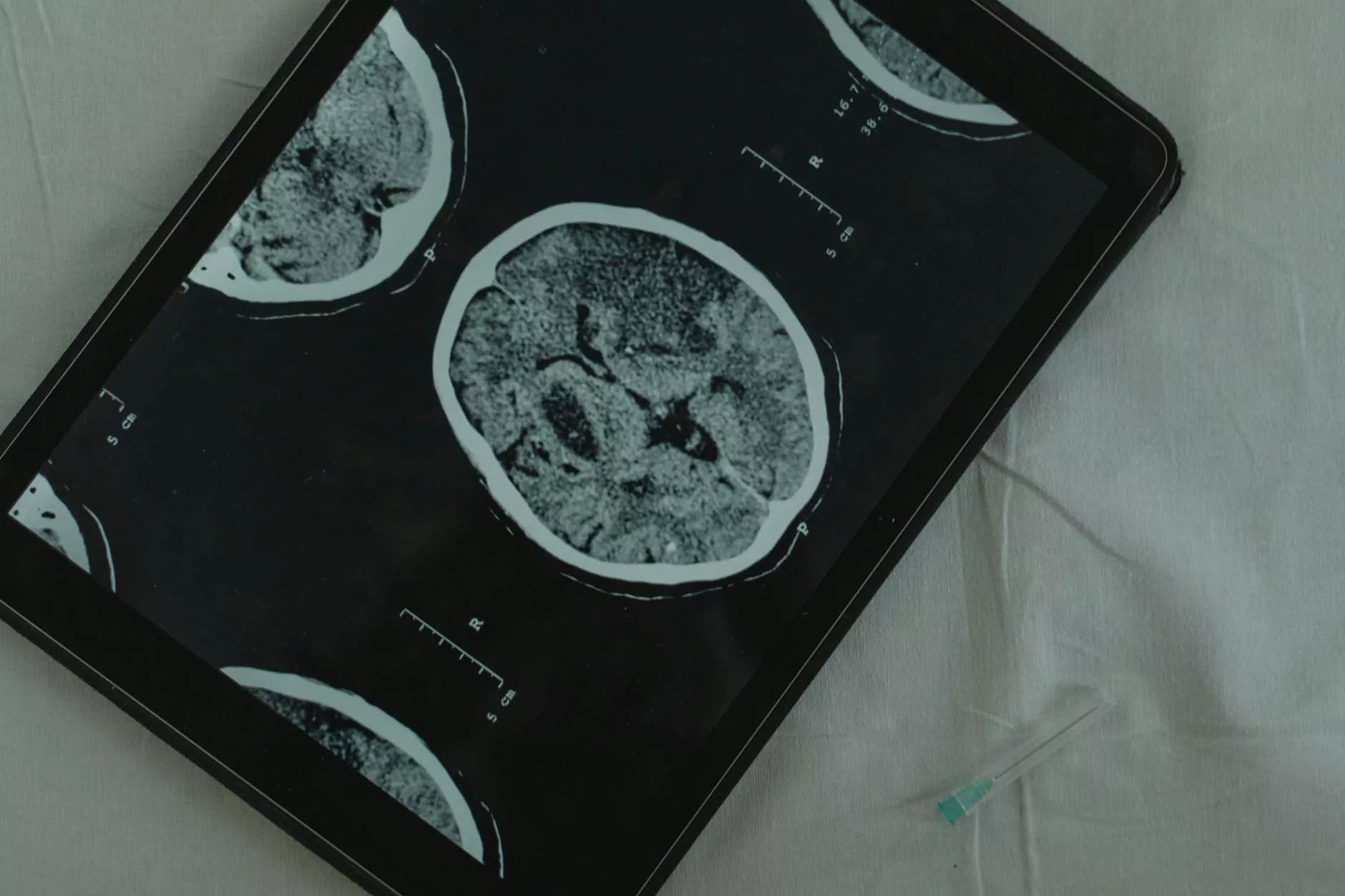
A CT scan, or computed tomography scan, uses X-rays to create detailed images of the inside of the body. Unlike standard X-rays, CT scans provide cross-sectional images, allowing medical professionals to see structures in the body in a more detailed and layered manner.
How CT Scans Work
- Multiple X-ray Images: The CT scanner takes numerous X-ray images from different angles.
- Computer Processing: A computer processes and compiles these images to create detailed cross-sectional images.
- 3D Imaging: Some advanced CT systems can even reconstruct the images into three-dimensional views for better assessment.
The Importance of CT Scans in Lung Cancer Diagnosis
The importance of CT scans in diagnosing lung cancer cannot be overstated. They are a critical component in the early detection, staging, and treatment planning for lung cancer.
Early Detection Saves Lives
Early-stage lung cancer often presents no symptoms. Regular screening with CT scans, especially for individuals at high risk (e.g., heavy smokers or those with a family history of lung cancer), can lead to earlier diagnosis. Studies show that low-dose CT screening can reduce lung cancer mortality significantly.
Staging of Lung Cancer
Once lung cancer is diagnosed, the next crucial step is staging, which determines the extent of the cancer in the body. CT scans help in identifying:
- The Size of the Tumor: Assessing the tumor's dimensions helps in determining the most appropriate treatment modality.
- Spread to Lymph Nodes: CT scans can help visualize lymph nodes in the chest to see if they are affected.
- Metastasis: CT imaging evaluates whether the cancer has spread to other organs.
Types of CT Scans Used in Lung Cancer Detection
There are various types of CT scans utilized in the detection and management of lung cancer:
1. High-Resolution CT (HRCT)
High-resolution CT scans offer a clearer and more detailed image of lung structures, making it an excellent tool for identifying small tumors and subtle parenchymal lung diseases.
2. Low-Dose CT (LDCT)
The low-dose CT scan is increasingly used for lung cancer screening due to its ability to reduce radiation exposure while still providing clear images for early detection.
CT Scan Procedure: What to Expect
Understanding the CT scan process can help alleviate any concerns or anxiety about the procedure. Here’s what you can expect during a typical CT scan for lung cancer:
- Preparation: You may be asked to avoid food or drinks a few hours before the scan. Inform your doctor about any medications or allergies.
- Positioning: You will lie down on a table, typically on your back. Straps may be used to help keep you in position.
- Scanning: The CT machine will rotate around you, capturing images. You will need to remain still and may be instructed to hold your breath at times to get clearer images.
- Post-Scan: Once the scan is complete, you can resume your normal activities. The images will be analyzed by a radiologist.
Risks and Considerations
While CT scans are generally safe, it's crucial to understand potential risks:
Radiation Exposure
The amount of radiation from a CT scan is higher than that of a standard X-ray. However, the benefits of early lung cancer detection usually outweigh the risks for high-risk individuals.
Incidental Findings
CT scans may reveal incidental findings, which can lead to unnecessary anxiety and additional testing. It’s essential to discuss these possibilities with your doctor beforehand.
Interpreting CT Scan Results
Once the scan is completed, a radiologist will interpret the images and prepare a report. The report will detail:
- Tumor Details: Size, shape, and location.
- Presence of Lymphadenopathy: swelling of lymph nodes.
- Additional Findings: Any other conditions that may be present in the lungs.
A multidisciplinary team, including oncologists, pulmonologists, and radiologists, will use this information to formulate a comprehensive treatment plan.
Follow-Up and Next Steps After a CT Scan
The follow-up process is vital in lung cancer management. Depending on the results of the CT scan, the following steps may be taken:
- Further Testing: Additional imaging tests, biopsies, or blood tests may be required.
- Treatment Options: Depending on the diagnosis, treatment options may include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or targeted therapy.
- Regular Monitoring: Continuous follow-up scans may be necessary to monitor tumor response or check for recurrence.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the CT scan for lung cancer plays a pivotal role in the early detection and management of lung cancer. Its ability to provide detailed imaging makes it an essential tool for healthcare providers in diagnosing and staging lung cancer accurately. If you or someone you know is at risk for lung cancer, discussing screening options like low-dose CT scans with a healthcare professional is vital.
Ongoing Research and Innovations As technology advances, the field of imaging continues to improve. Innovations, such as artificial intelligence in imaging analysis, promise to enhance the accuracy of diagnosis and further tailor treatment strategies for patients. Staying informed and proactive is key in the fight against lung cancer.
For more detailed information about lung cancer detection and treatment options, please visit the website of Hello Physio, an esteemed provider in the fields of health & medical services, sports medicine, and physical therapy.